Fundamentals of Vacuum Pumps (Low to Medium Vacuum)
What is Gas Ballast Valve?
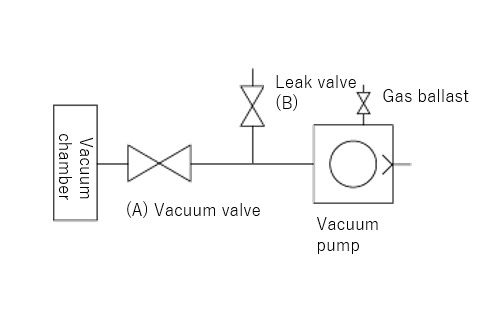
Gas Ballast Valve
After condensable gas is sucked, it is liquefied in the compression and pressurization process of the pump and mixes into the pump oil. It starts circulating in the pump together with the oil. In this situation, the pump's ultimate pressure reaches high, as it does when using oil with high vapor pressure--also, the lubricating ability of the oil decreases, which shortens the life of the shaft seal.
If air or dry nitrogen inflows from the gas ballast valve before the pump compresses and pressures, the condensable gas is not liquefied and is exhausted with the air or dry nitrogen through the exhaust valve.
When using a gas ballast valve, the greater "gas ballast effect" can be obtained when the higher pump temperature. To raise the pump temperature to approximately 70 ℃ before sucking condensable gas, open and operate the valve for 20 minutes. At low temperatures, the "gas ballast effect" is below processing capacity.
When the gas ballast valve should be open, and the condensable gas is not sucked, the pump oil scatters, power loss occurs, and the ultimate pressure gets high.
The capability of the gas ballast valve to process condensable gas is limited. After exhausting a large amount of condensable gas (air or gas containing a small amount of moisture or other vapor that contaminates the oil) without opening the gas ballast valve, the condensable gas remains in the pump oil.
In this case, when the gas ballast valve is open in operation, the oil temperature rises, and the gas ballast effect cleans the pump oil. While the gas ballast valve closes, continue this process until pressure reaches the target value.
If the purification does not progress after a long time, replacing the pumps is a sign.
Fundamentals of Vacuum Pumps (Low to Medium Vacuum)
HOW TO
- Vacuum Tech Basics
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Pumps (Low to Medium Vacuum)
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Pumps (High Vacuum)
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Valves
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Gauges
- Fundamentals of Quartz Crystal Oscillation Type Deposition Controller
- Fundamentals of Leak Detection
- Fundamentals of High-Speed Spectroscopic Ellipsometer
- Fundamentals of Gas Analyzer (Process Gas Monitor)
- The Others
- How to Choose The Best Products
- Old Models vs. New Models
- Troubleshooting