Fundamentals of Vacuum Pumps (High Vacuum)
Sorption Pump
What is a Sorption Pump?
Sorption pumps work with gas condensation at low temperatures like cryopumps. Sorption, as this name means adsorption.

Sorption Pump's Applications:
- Accelerators
- Electron Microscopes
- Analytical Instruments
Feature
This pump absorbs gas molecules and exhausts them by cooling a porous absorbent with a large specific surface with liquid nitrogen. Absorbents are activated carbon and molecular sieves which surfaces are about 500 m3/1gram. This can perform rough pumping from the atmospheric pressure and generates clean vacuum.
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
| Exhausting from the atmospheric pressure and reach an oil-free vacuum. | After pumping a certain amount of inert gas such as hydrogen, helium, and neon, Regeneration is required. |
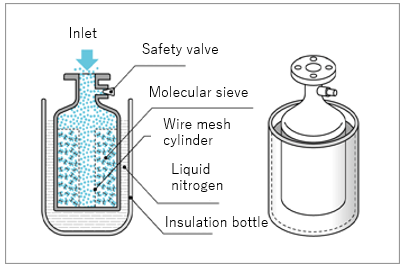
How Sorption Pump Works
The gas drawn through the inlet part inflow into a chamber with a porous adsorbent, Molecular Sieves. The molecular sieves cooled by the liquid nitrogen outside the chamber adorbs the gas in the chamber. Finally, the inside of the pump is evacuated.
Fundamentals of Vacuum Pumps (High Vacuum)
- Screw Pump
- Multi-Stage Roots Vacuum Pump
- Dry Scroll Vacuum Pump
- Dry Diaphragm Vacuum Pump
- Dry Rocking Piston Vacuum Pump
- Dry Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump
- Oil Rotary Vacuum Pump
- Mechanical Booster Pump
- Cryopumps
- Turbomolecular Pump
- Ion Pump
- Titanium Sublimation Pump
- Sorption Pump
- Diffusion Pump
- Ejector Pump
HOW TO
- Vacuum Tech Basics
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Pumps (Low to Medium Vacuum)
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Pumps (High Vacuum)
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Valves
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Gauges
- Fundamentals of Quartz Crystal Oscillation Type Deposition Controller
- Fundamentals of Leak Detection
- Fundamentals of High-Speed Spectroscopic Ellipsometer
- Fundamentals of Gas Analyzer (Process Gas Monitor)
- The Others
- How to Choose The Best Products
- Old Models vs. New Models
- Troubleshooting