Fundamentals of Vacuum Pumps (High Vacuum)
Turbomolecular Pump
What is a Turbomolecular Pump?
A turbomolecular pump consists of a rotor as a rotor blade with turbine-shaped blades and a stator as a flexed blade. The performance has developed recently, getting attraction.

Turbomolecular Pump's Applications:
- Semiconductor manufacturing equipment
- Deposition equipment
- Sputtering equipment
- Analysis equipment
- Etching equipment accelerator
- Flat Panel Display manufacturing equipment
Feature
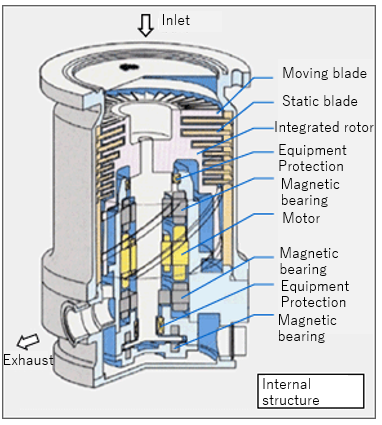
The turbomolecular pump consists of rotating blades at high speed and fixed blades. The rotating blades rotate tens of thousands of times/sec. The load (resistance) in the air damages them.
Therefore, the turbomolecular pump must work in a vacuum atmosphere, so fore vacuum pumps such as dry pumps pr rotary pumps are necessary.
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
| Constant pumping speed and gas pumping in the molecular flow region. No maintenance; Regeneration work. Allow Flammable and corrosive gas exhausted. |
Blades rotating at high speed. |
How Turbomolecular Pump Works?
When gas molecules inflow the pump's inlet port, the rotating blades at high speed give the gas molecules momentum and push them to the lower stage. The gas molecules are compressed through multiple compression stages and flow to the exhaust port.
Fundamentals of Vacuum Pumps (High Vacuum)
- Screw Pump
- Multi-Stage Roots Vacuum Pump
- Dry Scroll Vacuum Pump
- Dry Diaphragm Vacuum Pump
- Dry Rocking Piston Vacuum Pump
- Dry Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump
- Oil Rotary Vacuum Pump
- Mechanical Booster Pump
- Cryopumps
- Turbomolecular Pump
- Ion Pump
- Titanium Sublimation Pump
- Sorption Pump
- Diffusion Pump
- Ejector Pump
HOW TO
- Vacuum Tech Basics
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Pumps (Low to Medium Vacuum)
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Pumps (High Vacuum)
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Valves
- Fundamentals of Vacuum Gauges
- Fundamentals of Quartz Crystal Oscillation Type Deposition Controller
- Fundamentals of Leak Detection
- Fundamentals of High-Speed Spectroscopic Ellipsometer
- Fundamentals of Gas Analyzer (Process Gas Monitor)
- The Others
- How to Choose The Best Products
- Old Models vs. New Models
- Troubleshooting